# 课程信息
参考资料:
- Bilibili: 2021 Winter 版 CS224W 课程视频
- 课程网站
# Introduction & Machine Learning for Graphs
slides 1.
# Why Graphs?
图机器学习为什么复杂?
- 图结构本身是复杂的,其可以具有任意的大小和复杂的拓扑结构,不像文本或图像一样具有空间局部性 (spatial locality).
- 图结构中不存在参考点,没有固定的操作顺序。
# Applications of Graph ML
# Different Types of Tasks
图学习的任务可以包含不同类型,例如点层级的 (node-level), 边层级的 (edge-level), 集群 / 子图层级的 (community/subgraph-level), 或是整个图层级的 (graph-level).
- Node classification: Predict a property of a node
- Example: Categorize online users / items
- Link prediction: Predict whether there are missing links between two nodes
- Example: Knowledge graph completion
- Graph classification: Categorize different graphs
- Example: Molecule property prediction
- Clustering: Detect if nodes form a community
- Example: Social circle detection
- Other tasks:
- Graph generation: Drug discovery
- Graph evolution: Physical simulation
# Example of Node-level ML Tasks: Protein Folding
对于已知的氨基酸序列,如何确定蛋白质的空间结构?
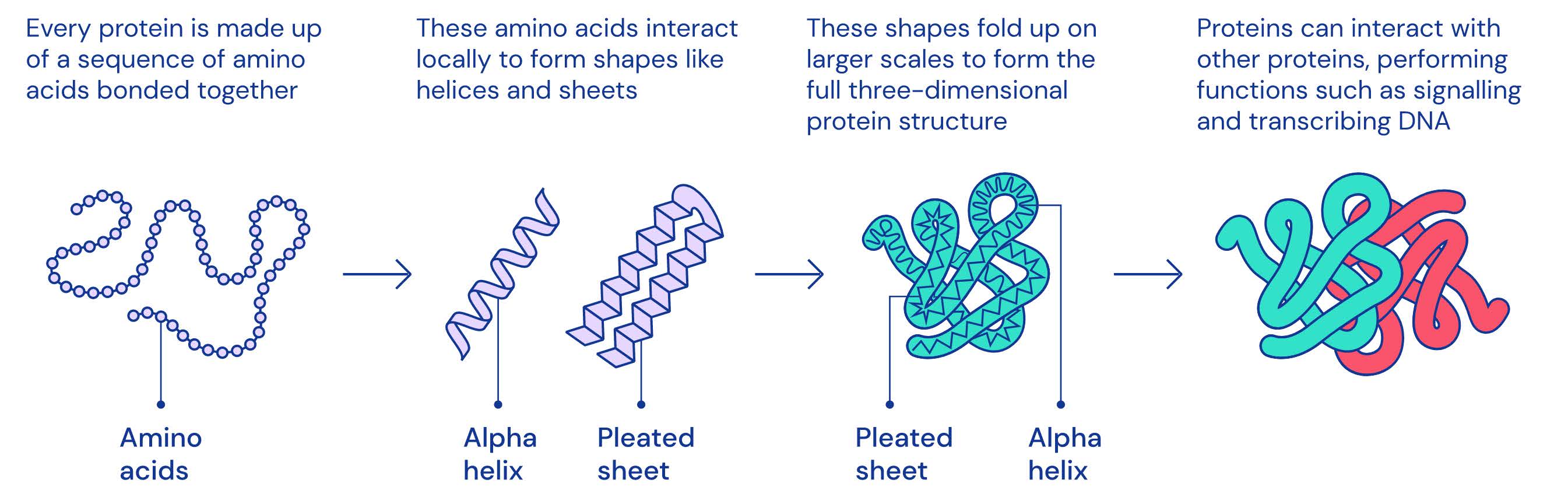
2020 年,DeepMind 提出的 AlphaFold 在蛋白质空间结构预测上的准确率已经达到 80%+, 这将大大提高药物的研发速度。
在 AlphaFold 中,图的顶点代表氨基酸 (amino acids)/ 残基 (residues), 图中的边代表氨基酸对在蛋白质结构中的接近程度 (Proximity between amino acids).
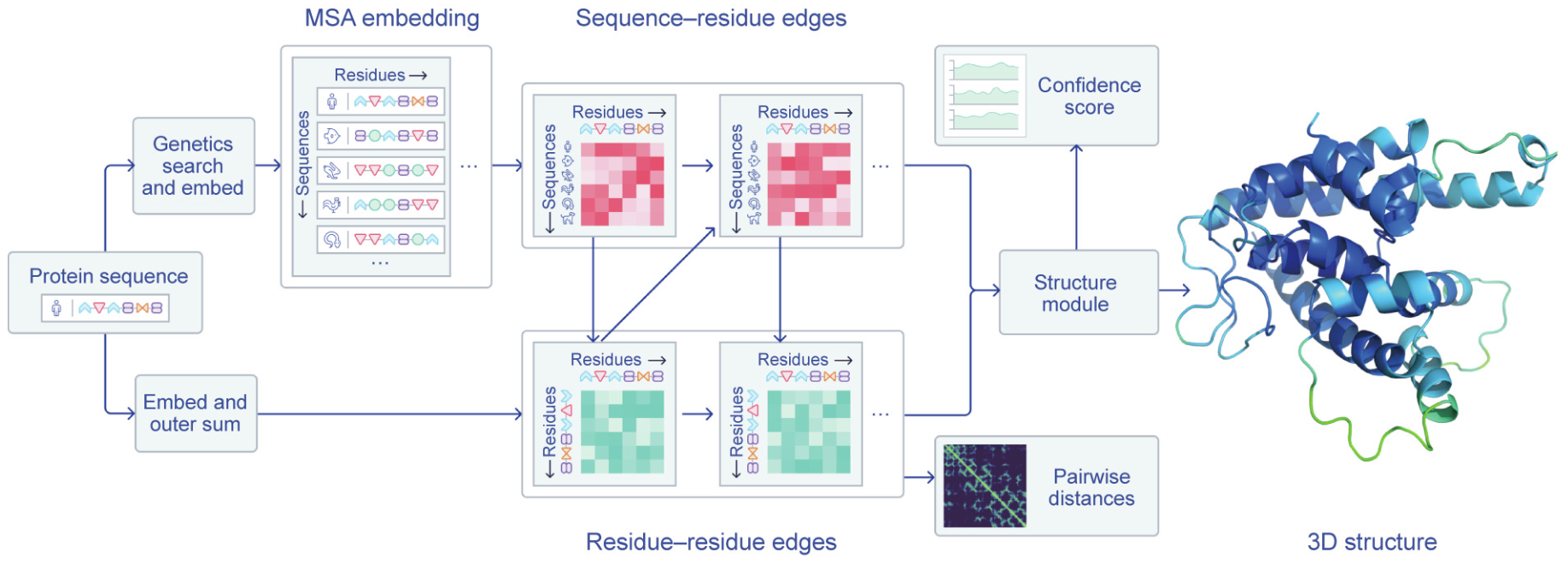
关于 AlphaFold 的更多介绍还可以参考:
- Google DeepMind 的博客:AlphaFold: a solution to a 50-year-old grand challenge in biology
- Deep Mind 发表在 Science 上的 Paper.
# Example of Edge-level ML Tasks(1): Recommender System
推荐系统中的
# Example of Edge-level ML Tasks(2): Drug Side Effects
# Example of Subgraph-level ML Tasks: Traffic Prediction
# Example of Graph-level ML Tasks(1): Drug Discovery
# Example of Graph-level ML Tasks(2): Physics Simulation
# Choice of Graph Representation
在这一部分中,Leskovec 讲述了图的基本构成原理以及一些特殊的图如何应用在具体的问题中。
# Components of a Netowrk
图中的对象包括:
- 节点 (nodes/vertices)
- 边 (links/edges)
- 图 (network/graph)
# Directed vs. Undirected Graphs
图包括有向图和无向图。有向图和无向图主要由数据集的性质决定。例如合作关系、朋友关系、蛋白质的相互作用可以用无向图建模,而电话拨打网络、Twitter 的关注关系可以用有向图建模。
# Node Degrees
顶点的度是顶点所连边的数量,可以记作 . 平均度可以采用 计算。此外,对于有向图,可以分为入度 (in-degree) 和出度 (out-degree), 分别记作 和 .
# Bipartite Graph
二部图是一种常用的图结构。例如:作者 - 论文网络、演员 - 电影网络等可以采用二部图建模。
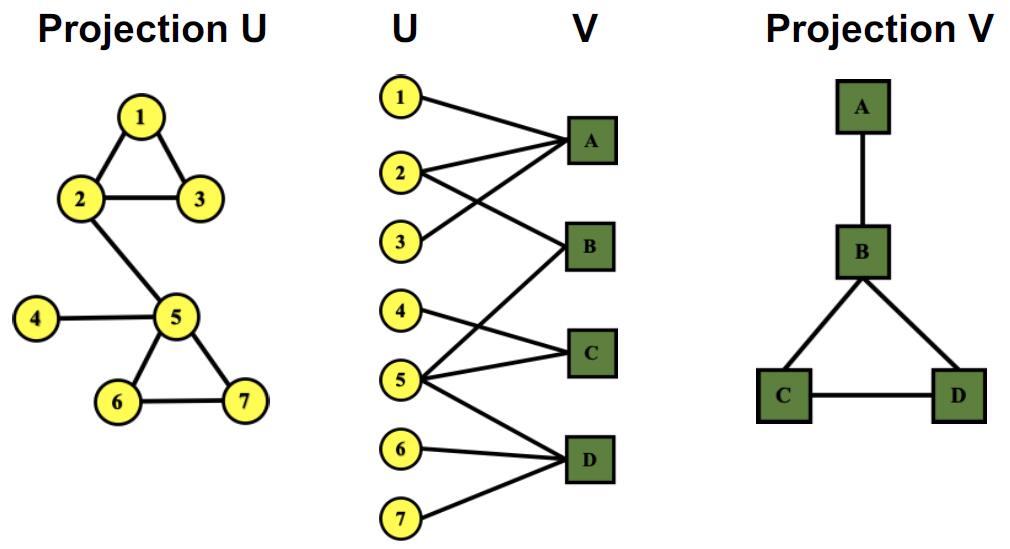
# Fold/Projected Bipartite Graph
对于二部图,可以将其中的某部分节点全部提取出来,并在有共同邻居的节点对间连边,这样就得到了二部图在一侧节点上的投影。
# Adjacency Matrix
邻接矩阵是一种图的表示方式。对于无向图,若 之间有连边,则令 . 对于有向图,若存在 的边,则令 .
如果图本身是有权重的,那么可以直接用权重代替邻接矩阵的 值。
需要注意的是,现实世界的网络大多是十分稀疏的。
# Edge List
采用边的列表也可以表示图。
# Adjacency List
邻接表也是一种重要的图表示方式。
# Node and Edge Attributes
图中的顶点和边可以具有多种附加属性,例如:
- 权重 (weight): 例如联系的频率
- 排序 (ranking): 最好的朋友、次好的朋友...
- 类型 (type): 朋友、亲戚、同事等
- 标志 (sign): 朋友 / 敌人,信任 / 不信任...
- 基于图结构的其它性质:两节点的共同邻居数等
此外,图本身也可以拥有某些性质,通常是图所表示的建模对象的性质,比如图所表示的分子性质等等。
# More Types of Graphs
图还有更多的分类,例如:
- 有权图 (weighted)/ 无权图 (unweighted)
- 有自环的图 (with self-loops)/ 无自环图
- 多重图 (multigraph)/ 简单图
- 多重图有时可以看作有权的简单图,但如果多重图的亮点间的不同边具有不同的性质,那么就需要对每条边分别表示。
# Connetcivity
无向图中的连通性是易于定义的。需要注意,非连通的无向图对应的临界矩阵可以重排为多个方阵组成的对角阵。
对于有向图,连通性分为两种:
- 强连通有向图 (strongly connected directed graph): 从任一节点到另一节点都存在一条通路
- 弱连通有向图 (weakly connected directed graph): 忽略边方向时可以看作无向连通图
对于非强连通的有向图,可以关注其强连通分支 (strong connected components, SCC).